Hearing test
If your child is referred for a hearing assessment, they will be seen by one or two members of the audiology team. The type of assessment they will have will depend on their age and ability. Audiology assessments can be categorized in to two main types; behavioural and objective assessments.
What is a behavioural assessment?
Behavioural tests need the child to be awake and paying attention as the child’s behaviour change in response to a sound is being assessed. The way we assess their behaviour change will be dependent on age and ability. Please see below for more information on age specific behavioural tests.
What is an objective assessment?
Objective tests, while still needing a certain amount of co-operation, need less input from the child. They can often be completed while asleep or if a child is not interested in interacting during the appointment. They are also often less age specific and can sometimes be completed at any age. Please see below for more information on objective tests.
What assessment will be completed on my child?
Age 0 to 4 months – Objective tests are completed with babies that are not yet able to give reliable behavioural responses to sound.
Age 4 to 8 months – This age group are sometimes too active for certain objective tests but are not yet ready for a full behavioural assessment. The assessments completed will be based on an individual basis and may be a combination of different objective assessments.
Age 8 to 30 months – Visual Reinforcement Audiometry (VRA)
This technique is used to measure the child’s Minimum Response Level at different pitches. The child is seated between visual reinforcement reward boxes, where speakers are attached to those boxes. To condition the child, a sound is played from the speaker and as the child turns to sound they are presented with a visual reward in the form of an illuminated toy in the box.
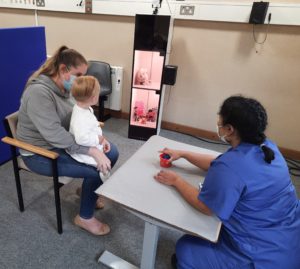
Age 30 months to 48 months – Play Audiometry
Play audiometry is preferred for children who can understand simple instructions and are able to physically complete a simple task. To determine the hearing threshold, a game is played in which children perform an action when sound is heard. This could take the form of putting toy men in the boat or stacking cups.
Practising ‘Ready, Steady … Go!’ games will help a child prepare for this type of test.
Age 48 months+ – Play audiometry with headphones or Pure Tone Audiometry (PTA)
Play audiometry is performed with headphones when children are able to tolerate keeping the headphones on for a prolonged time. This suggests they are ready for ear specific testing. Play audiometry is completed with a game task, i.e. man in the boat or other game.
PTA is completed with a button press response.

What other hearing tests do we do?
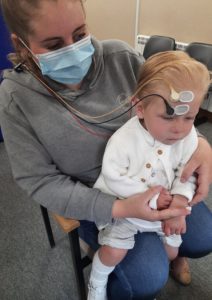
- Auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing measures the response to sound along the auditory nerve. A child needs to be very still and settled for this test, ideally asleep. The appointment can take up to 2 hours and is most commonly completed with new-born babies, but can be completed at other ages when necessary.
.
- Otoacoustic emission testing measures the response from the outer hair cells in the inner ear. It usually takes a few minutes if child is quiet and still.

- Tympanometry: Measures eardrum movement in response to pressure and can tell us if a child has any middle ear fluid (glue ear).
- Middle ear reflex: testing measures the contraction of a middle ear muscle in response to louder sounds. The audiologist will carry out this test during the appointment if required.

